Biomass stoves represent a fascinating intersection of traditional heating methods and modern concerns about renewable energy and energy efficiency. They offer a way to heat your home using readily available organic materials, potentially saving you money on your utility bill and reducing your reliance on fossil fuels. Understanding how these stoves work, their benefits, and their drawbacks is crucial before considering one for your home. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know, and also point you to possible energy assistance programs that can help with the initial investment.
Understanding Biomass Stoves: A Definition
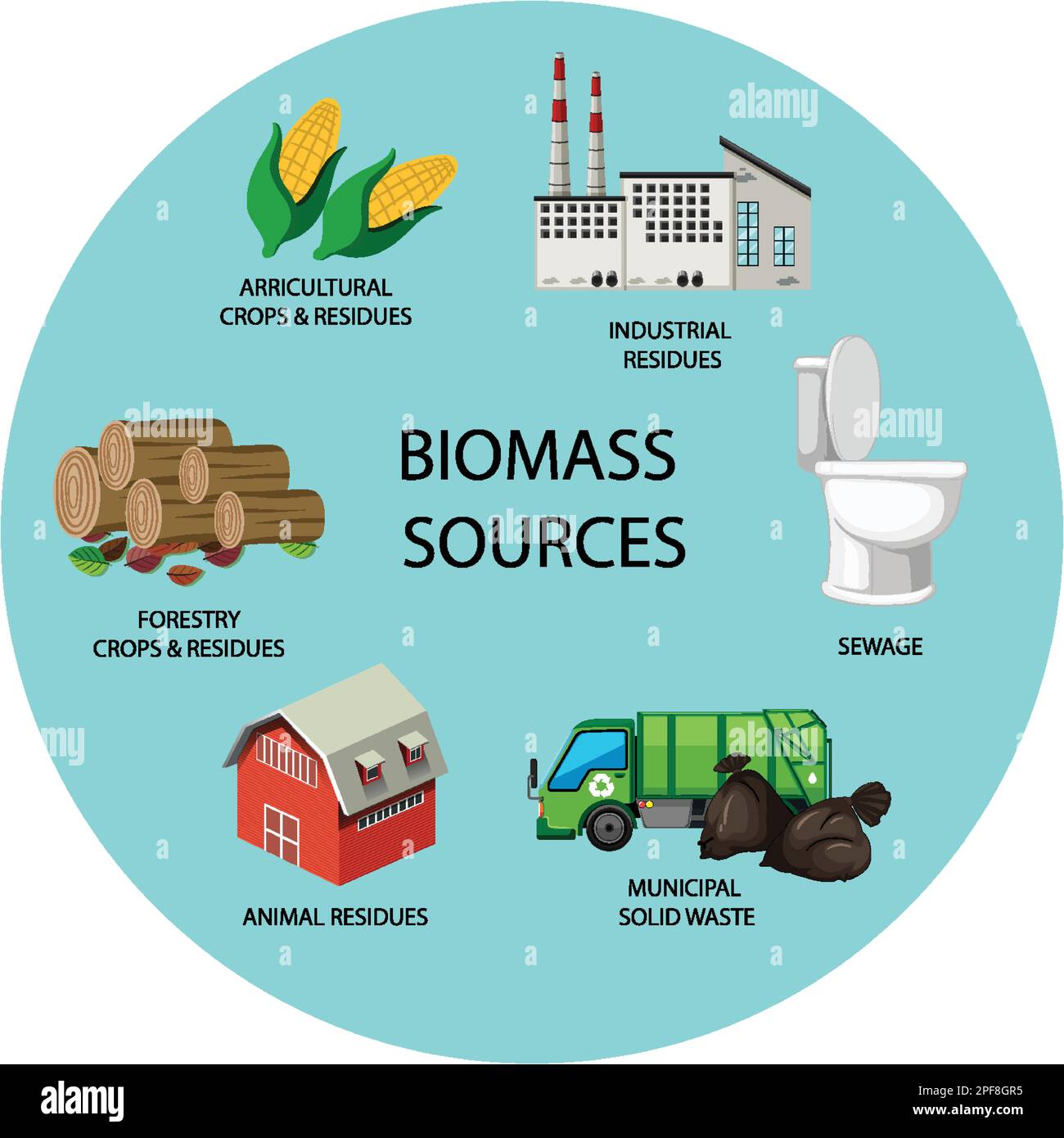
A biomass stove is a heating appliance that burns organic matter, known as biomass, to generate heat. This biomass can take many forms, including wood pellets, wood chips, cordwood, agricultural residues (like corn stalks or wheat straw), and even specially grown energy crops. Unlike traditional wood-burning stoves, many modern biomass stoves are designed for greater efficiency and cleaner burning. They offer an alternative to conventional heating systems powered by natural gas, propane, or electricity. If you’re struggling with your energy bills, exploring renewable energy options like biomass could also lead you to discover various low income energy programs or even energy rebates that can help offset costs.
How Biomass Stoves Work: The Combustion Process
The operation of a biomass stove involves a controlled combustion process to extract heat from the fuel. Here's a breakdown of the typical stages: Fuel Loading:Biomass fuel is loaded into the stove's hopper or firebox. Some stoves require manual loading, while others feature automated feeding systems for consistent fuel supply.
Ignition: The fuel is ignited, typically with an electric igniter or a manual fire starter. Once lit, the combustion process begins, releasing heat and gases.
Combustion: The heart of the stove, where the fuel burns. Airflow is carefully regulated to ensure efficient and complete combustion. More advanced models use multiple air inlets to optimize the air-to-fuel ratio, minimizing emissions and maximizing heat output.
Heat Exchange: The heat generated by combustion is transferred to the surrounding environment through convection and radiation. Some stoves also incorporate heat exchangers to further improve efficiency by extracting more heat from the exhaust gases.
Exhaust: The exhaust gases, containing combustion byproducts, are vented outside the building through a chimney or flue. Modern biomass stoves often include catalytic converters or other emission control technologies to reduce pollutants.
Ash Removal: As biomass burns, it leaves behind ash. Regular ash removal is necessary for optimal stove performance. Some stoves have self-cleaning mechanisms to simplify this process.
Types of Biomass Stoves: Choosing the Right One for Your Needs
Biomass stoves come in various designs, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types include: Wood Stoves:The most traditional type, burning cordwood. These can be very affordable but often require more manual labor (splitting and stacking wood) and tend to be less efficient than pellet stoves. Look for EPA-certified models for cleaner burning. If you’re on a tight budget, keep an eye out for fuel assistance checks that might help cover the cost of firewood.
Pellet Stoves: These stoves burn compressed wood pellets, which are a consistent and relatively clean-burning fuel source. Pellet stoves typically have automatic feeding systems and offer precise temperature control. They are generally more expensive than wood stoves but offer greater convenience and higher efficiency. Many states offer energy rebates for installing high-efficiency pellet stoves.
Corn Stoves: Similar to pellet stoves, corn stoves burn dried corn kernels. They can be a cost-effective option in regions where corn is readily available. However, they may require more frequent cleaning than pellet stoves, and not all corn varieties are suitable for burning.
Multi-Fuel Stoves: These stoves can burn a variety of biomass fuels, including wood pellets, corn, and other agricultural residues. They offer flexibility in fuel selection but may require adjustments for optimal performance with different fuels.
Benefits of Using a Biomass Stove: A Sustainable Heating Solution
Biomass stoves offer several compelling advantages, making them an attractive heating option for many homeowners: Renewable Energy Source:Biomass is a renewable resource, unlike fossil fuels. Sustainable forestry practices ensure that wood is harvested responsibly, and agricultural residues are a byproduct of food production.
Cost Savings: Depending on the cost of biomass fuel in your area, a biomass stove can potentially save you money on your heating bill compared to oil, propane, or electricity. Exploring DIY energy efficiency measures can also help you reduce your overall energy consumption.
Reduced Carbon Footprint: Biomass combustion can be carbon neutral if the carbon dioxide released during burning is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the biomass during its growth.
Energy Independence: Using locally sourced biomass fuel reduces reliance on foreign energy sources, promoting energy independence.
Home Heating Programs: Many local and federal programs exist to help with the cost of heating, especially during winter. Some biomass stoves might qualify under certain home heating programs.
Off-Grid Capability: Some biomass stoves can operate without electricity, providing a reliable heating source during power outages.
Drawbacks of Using a Biomass Stove: Considerations Before Investing
Despite their advantages, biomass stoves also have some drawbacks that need to be considered: Fuel Storage:Biomass fuel requires storage space, which can be a concern for homeowners with limited space.
Maintenance: Biomass stoves require regular maintenance, including ash removal and cleaning of the chimney or flue.
Emissions: While modern biomass stoves are designed to minimize emissions, they still produce some air pollutants. It's crucial to choose an EPA-certified model and ensure proper installation and maintenance to minimize environmental impact.
Initial Investment: The initial cost of a biomass stove can be higher than that of some conventional heating systems, although this cost can be offset by long-term fuel savings. Explore available energy rebate programs, including HVAC tax credits, to potentially reduce the initial cost.
Fuel Sourcing: Sourcing biomass fuel can be challenging in some areas. Ensure a reliable supply of affordable fuel is available before investing in a biomass stove. Contacting your local utility company can sometimes provide information on fuel suppliers or even connect you with relevant energy assistance programs.
Installation and Safety Considerations: Protecting Your Home and Family
Proper installation and safety precautions are essential when using a biomass stove: Professional Installation:It's highly recommended to have a qualified professional install your biomass stove to ensure proper venting and compliance with local building codes.
Chimney Inspection: Ensure your chimney is in good condition and properly sized for the stove. Have it inspected and cleaned regularly by a certified chimney sweep.
Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home to alert you to the presence of this deadly gas.
Smoke Detectors: Ensure smoke detectors are properly installed and functioning correctly.
Clearance to Combustibles: Maintain adequate clearance between the stove and any combustible materials, such as walls, furniture, and curtains.
Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in the room where the stove is located to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide.
Financial Assistance and Incentives: Making Biomass Stoves More Affordable
Several financial assistance and incentive programs can help make biomass stoves more affordable: Federal Tax Credits:Check for federal tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements, including biomass stoves.
State and Local Rebates: Many states and local governments offer rebates for installing biomass stoves. Contact your state energy office or local utility company for information on available programs. You can also look for energy saving plans offered by your utility provider.
LIHEAP (Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program): LIHEAP provides assistance to low-income households with their energy bills. In some cases, LIHEAP funds can be used to purchase or repair heating equipment, including biomass stoves.
HEAP (Home Energy Assistance Program): Similar to LIHEAP, HEAP offers assistance with home energy costs, potentially including the purchase of efficient heating systems like biomass stoves.
Utility Bill Assistance: Contact your local utility company to inquire about utility bill assistance programs and payment plans.
The Future of Biomass Stoves: Innovation and Sustainability
Biomass stove technology is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and development focused on improving efficiency, reducing emissions, and expanding the range of usable biomass fuels. Innovations such as advanced combustion controls, automated fuel feeding systems, and improved emission control technologies are making biomass stoves an even more attractive and sustainable heating option.
As concerns about climate change and energy security continue to grow, biomass stoves are likely to play an increasingly important role in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. By understanding the principles of biomass stove operation, considering the benefits and drawbacks, and taking advantage of available financial assistance programs, you can make an informed decision about whether a biomass stove is the right heating solution for your home. Remember to consider DIY energy efficiency measures in conjunction with a new heating system to maximize energy savings and potentially lower your utility bill even further. Also, keep an eye out for any HVAC tax credits that might be available for installing a more energy-efficient heating system.